GenAI Models
[Survey] A Survey of Reshaping the GenAI Research Landscape🔗
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.10868 18 Dec 2023 IEEE
This survey explores Generative AI (AI), focusing on Mixture of Experts (MoE), multimodal learning, and the path towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
Text & Multimodal LLMs🔗
[Mixtral] Mixtral of Experts🔗
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.04088 8 Jan 2024 Mixtral.ai
We introduce Mixtral 8x7B, a Sparse Mixture of Experts (SMoE) language model. Mixtral has the same architecture as Mistral 7B, with the difference that each layer is composed of 8 feedforward blocks (i.e. experts).
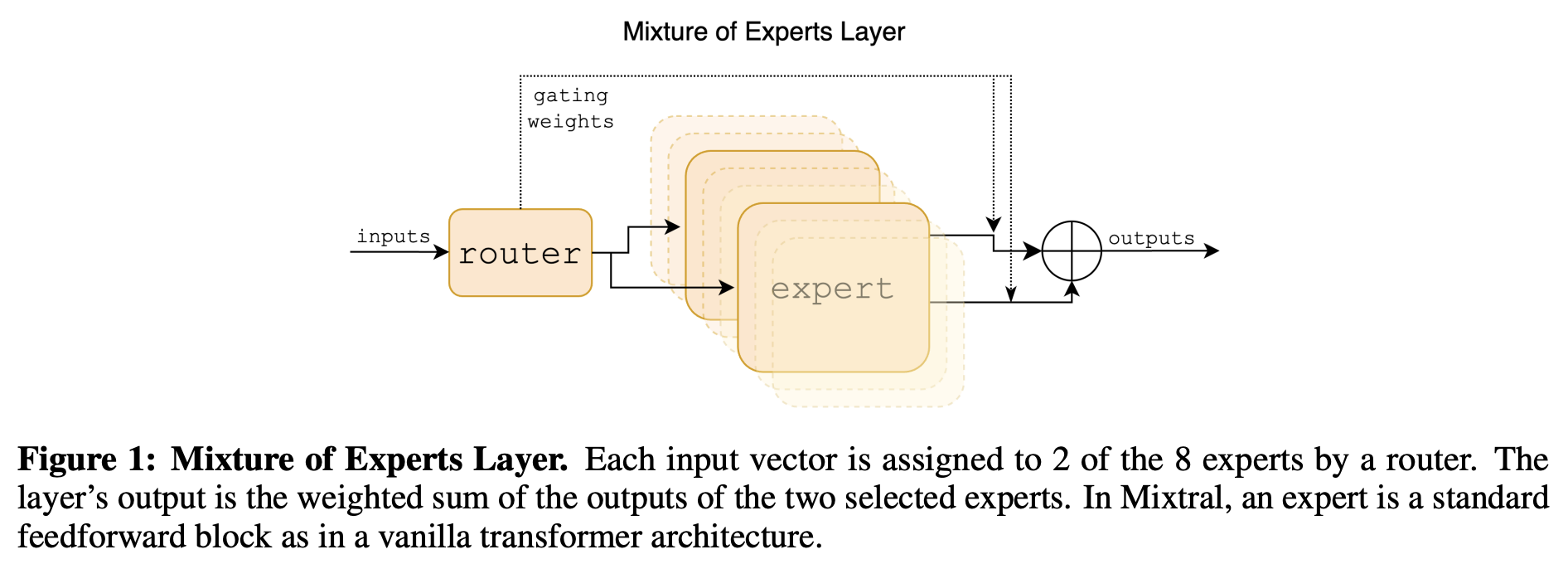
- G denotes n dimensionality of the gating network (router), E is the expert network.
Consecutive tokens are often assigned to the same experts. In fact, we observe some degree of positional locality in The Pile datasets. Table 5 shows the proportion of consecutive tokens that get the same expert assignments per domain and layer. Figures are not showing it clearly.

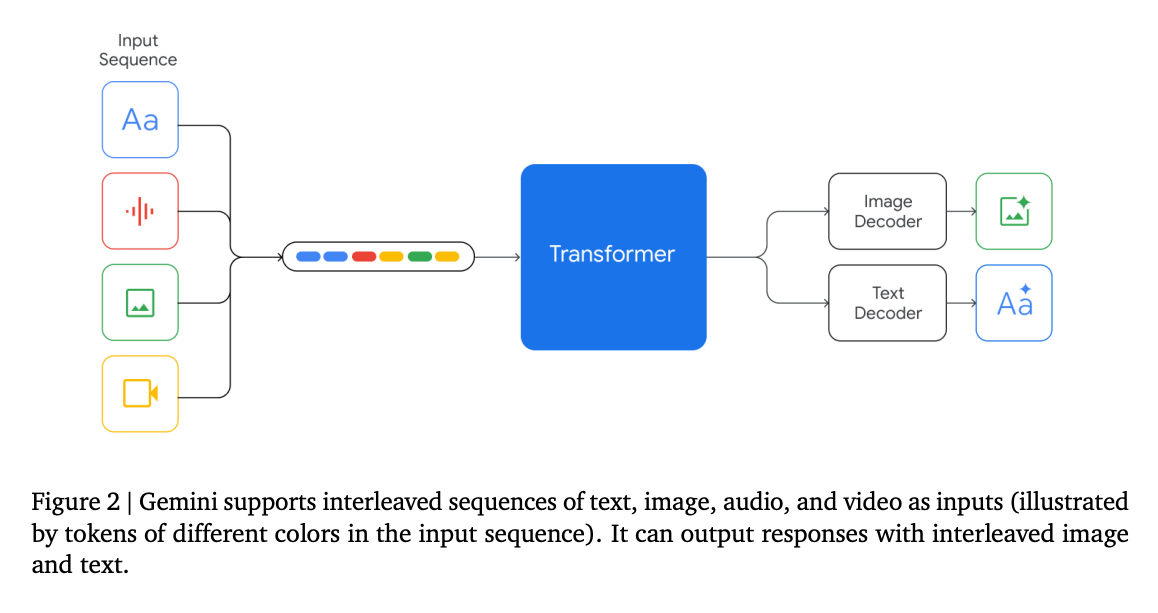
[Gemini] A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models🔗
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.11805 19 Dec 2023 Google
The reasoning capabilities of large language models show promise toward building generalist agents that can tackle more complex multi-step problems.
[ModernBERT] Modern Bidirectional Encoder🔗
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.13663 18 Dec 2024
The paper introduces ModernBERT, a new family of encoder-only transformer models that brings modern optimizations to BERT-style architectures.
Key Features:
-
Architectural Improvements:
- Uses GeGLU activation
- RoPE positional embeddings
- Alternating local-global attention
- Native 8192 sequence length
- Optimized for efficient inference on common GPUs
- Full model unpadding for better efficiency
-
Training:
- Trained on 2 trillion tokens
- Includes code data in training mixture
- Uses modern BPE tokenizer with 50,368 vocabulary size
-
Unique Advantages:
- Successfully combines modern LLM architecture improvements with encoder-only models
- Achieves better performance while maintaining high efficiency
- Represents first major Pareto improvement over older encoders like BERT
- Code-Aware Design: Uses a code-aware tokenizer that can properly handle programming syntax
- The code training makes ModernBERT uniquely suited for code-related tasks while maintaining strong performance on traditional NLP tasks
Limitations:
- MLM-only objective (Masked Language Modeling)
- Not trained with RTD (Replaced Token Detection) which might hurt classification results
[GLiNER] Generalist Model for NER using Bidirectional Transformer🔗
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.08526 14 Nov 2023
flowchart LR
Text[Input Text] --> Enc[Bidirectional\nEncoder]
Types["Entity Types\n(any types)"] --> Enc
Enc --> Spans[Span\nRepresentations]
Enc --> Entities[Entity\nRepresentations]
Spans --> Match{Match in\nLatent Space}
Entities --> Match
Match --> NER["Named Entities\n(Parallel Extraction)"]
style NER fill:#c8e6c9,color:#000
Key Points:
Problem & Solution:
- Traditional NER models are limited to predefined entity types
- GLiNER introduces a compact model that can identify any type of entity
- Uses bidirectional transformer encoder for parallel entity extraction
Architecture:
- Uses bidirectional transformer (like BERT/DeBERTa) as backbone
- Components:
- Pre-trained textual encoder
- Span representation module
- Entity representation module
- Treats NER as matching entity types with text spans in latent space
Performance:
- Parallel entity extraction vs sequential generation in LLMs
- Compact design (50M-300M parameters) vs billions in LLMs
- Effective negative entity sampling during training
- Entity type dropping as regularization technique
Limitations:
- Lower performance on informal text (e.g., tweets)
- Reduced effectiveness on non-Latin scripts
- Room for improvement in low-resource languages
Vision & Diffusion Models🔗
Training Diffusion Models with RL🔗
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.13301 22 May 2023
- Normalization over contrastive prompts.
- Prompt synthesis via LLM.
- Incorporating textual inconsistency into the score (calculate distance in embedding space) - avoid synthetically close, semantically different.
[DPOK] RL for Fine-tuning Text-to-Image Diffusion Models🔗
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.16381 25 May 2023
We focus on diffusion models, defining the fine-tuning task as an RL problem, and updating the pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models using policy gradients to maximize the feedback-trained reward. Our approach, coined DPOK, integrates policy optimization with KL regularization.
Generation of more data includes generating n-1 negative samples and leveraging contrastive loss and generating more images to increase diversity.
In fine-tuning the loss function will be the expectancy of the sum of all the binary-human-classified dataset and also loss from the pre-training based data (weighted with B) to maintain accuracy of the model (avoid catastrophic forgetting). For the reward loss the idea is for the reward to be log-likelihood but it’s not easy, Therefore we minimize reward-weighted MSE loss instead.
Setup: Pretrained Stable Diffusion 1.5, fine-tuning using static CLIP language encoder, Reward model is MLP using ViT-L/14 CLIP for image/text embeddings, Dataset 2700 prompts, 27k images, 16k unlabeled and 625k for pretraining.
SFT: model is updated on a fixed dataset generated by the pre-trained model.
RL: model is updated using new samples from the previously trained model during online RL fine-tuning.
Based on the results, adding KL regularization helps in improving both image fidelity and accuracy (mostly image fidelty).
[Point-E] A System for Generating 3D Point Clouds from Complex Prompts🔗
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.08751 16 Dec 2022 OpenAI
In this paper, we explore an alternative method for 3D object generation which produces 3D models in only 1-2 minutes on a single GPU. Our method first generates a single synthetic view using a text-to-image diffusion model, and then produces a 3D point cloud using a second diffusion model which conditions on the generated image.
Using glade dataset for 2D (fine-tuned on 3D rendering).
[CLIP] Connecting text and images🔗
Arxiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020 26 Feb 2021 OpenAI
CLIP pre-trains an image encoder and a text encoder to predict which images were paired with which texts in our dataset. We then use this behavior to turn CLIP into a zero-shot classifier. We convert all of a dataset’s classes into captions such as “a photo of a dog” and predict the class of the caption CLIP estimates best pairs with a given image.